
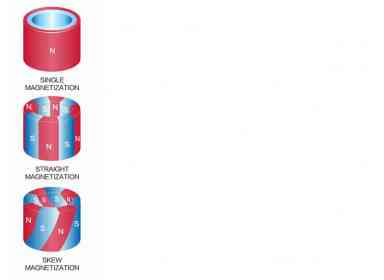
Sintered radial neodymium iron boron ring magnets are oriented by radial alignment of powders. It can be straight, skew or unipole magnetized. There are two production methods - sintered powder or hot press (MQ3) method. Compared to traditional arc magnets or IPM (internal permanent magnet
iron boron ring magnets are oriented by radial alignment of powders. It can be straight, skew or unipole magnetized. There are two production methods - sintered powder or hot press (MQ3) method. Compared to traditional arc magnets or IPM (internal permanent magnet ) assemblies, radial rings can improve motor performance and increase yields over traditional motor assembly methods. These magnets are widely used in DC brushless and servo motors for robotic and automotive applications.
) assemblies, radial rings can improve motor performance and increase yields over traditional motor assembly methods. These magnets are widely used in DC brushless and servo motors for robotic and automotive applications.